What is spasmodic dysphonia?
Spasmodic dysphonia is a voice disorder caused by the excessive
tension in the laryngeal muscles. Individuals with spasmodic dysphonia
have breaking voices and face difficulty to start and continue communication.
Spasmodic dysphonia causes a problem in muscle tension and its
name is being in use when diagnosing the dystonia problem.
Especially this can affect one’s verbal ability as inadequate tension and
strains could affect the phonatory pattern. From time to time, focal
laryngeal dystonia can be accompanied as its main symptom.
The number of people suffering spasmodic dysphonia of unknown
origin in U.S. ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 based on the
U.S .statistics. Korea has no accurate statistical data on spasmodic
dysphonia, but the number is assumed to be from 2000 to 3000.
Spasmodic dysphonia is often classified according to the age these
symptoms develop. When symptoms develop before the age of 20, it
is called infant type. When symptoms develop after the age of 20, it is
called adult type.
Main cause of spasmodic dysphonia
Many doctors thought mental problems were the cause of spasmodic dysphonia, because symptoms would get better when taking alcohol or tranquilizers, or get worse when being stressed or talking on the phone.
In the 1980’s, as researches of the cranial nerve brought the thought that the cause of spasmodic dysphonia was the abnormal spasm of the laryngeal muscles due to the inharmonic function with the basal ganglia where the integration of the central nerves takes place.
Dr. Ludlow, from the National Institute of Neurologic Disorder (NINDS) of National Institute of Health (NIH), proved that the cause of spasmodic dysphonia is the abnormal nerve system in the Nucleus Tractus of Solitarius, so patients lose control of their vocal fold muscle which makes it hard to talk and breaks off sounds.
Types of Spasmodic Dysphonia
Adductor type

Abductor type
- Glottic type
- Supraglottic type
- Dystonia tremor
- Adductor type with tremor
Mixed type
(mixed type)

Respiratory Dysphonia
(respiratory)

- Abductor-adductor type
(abductor type with symptoms of adductor type)
- Adductor-abductor type
(adductor type with symptoms of abductor type)
Spasmodic Dysphonia Examinations
First, you will receive an acoustic vocal test. Then a test will be performed to measure the muscular spasm of vocal
cord when speaking, and examine excessive spasm or tremor of the laryngeal muscle using a laryngoscope.
Next, we will measure the changes in the basic vocal frequency with acoustic tests and observe the vocal waveform through spectrogram.
Then we run the electro-glottography test and measure the resistance of the larynx through the aero dynamics test.
Laryngeal stroboscopy examines the movement of the larynx, and the laryngeal electromyography helps find the
abnormal movements of the larynx and vocal fold muscle. Especially using the laryngeal electromyography we can
find pathophysiological problems and estimate the possibilities of recovery by checking laryngeal reflex.
We also use the high speed vocal fold filming system which was introduced for the first time in Asia, to find the
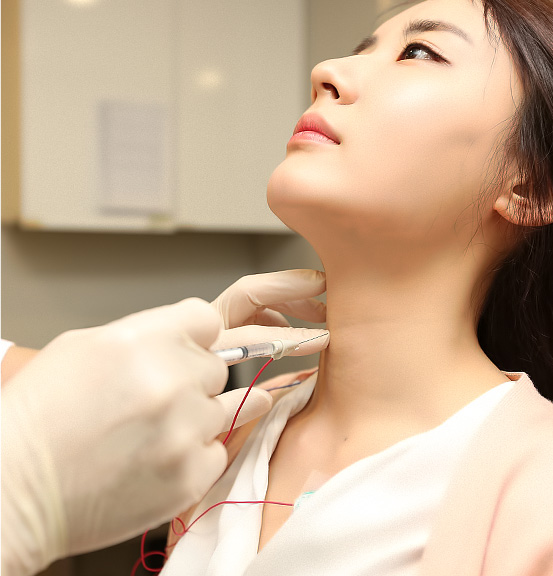
exact place of spasm. Botulinum Toxin injection, where a small quantity of Botulinum Toxin is directly injected to the affected muscle,
enables the voice to stay in good condition without the period of hoarseness.
 Using electromyography for Spasmodic Dysphonia
Using electromyography for Spasmodic Dysphonia
 Psychoacoustic evaluation
Psychoacoustic evaluation
 Stroboscopy
Stroboscopy
 High Speed Evaluation System
High Speed Evaluation System
Ways to treat spasmodic dysphonia
 Medicinal treatment
Medicinal treatment
In general, anti-choline type drug, tranquilizer, baclofen, dopamine antagonist and etc are often used.
However, medicinal treatment has serious side effects and is used only for serious myotonic disorders. Medicine treatment for spasmodic dysphonia is just secondary treatment.
 Botulinum Toxin Treatment
Botulinum Toxin Treatment
The injection of botulinum toxin (Botulinum Toxin) is currently the most effective treatment
However, this is a temporary treatment which improves the voice for a period
of three to six months after which the voice symptoms gradually return.
The treatment requires continual injections to maintain a good speaking voice.
A high level of skilled experience with electromyography is required to perform the Botulinum Toxin injection to maintain the
effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin and to shorten the period of hoarseness period. This way it could normalize the
dystonia pattern through controlling the cerebral nerve reflex system.
The strength of this treatment is the more this treatment is done the less frequent Botulinum Toxin treatment is required.
As a result, about 60% of patients have treated Spasmodic Dysphonia completely within 3~4 years.
This treatment is being performed in Yeson Voice Center with a high successful rate.
Click here to find more information about Botulinum Toxin treatment
 Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment
- Hemilaryngectomy
- Thyroid
chondroplasty - Laser vocalis muscle cordotomy
- Nerve stimulator transplantation
Professor Dedo has firstly performed Hemilaryngectomy in
1976 but due to high recurrent level and deteriorated
symptom it’s not being performed anymore.
Since then Dr. Tucker has firstly performed Thyroid chondroplasty
in 1989 and Dr. Isshiki has performed similar procedure since 2000.
However, the result was not as good as expected according to the long-term track
of outcome presented in the best ENT Journal, Laryngoscope
(It is stated that only about 33% of patients
who had surgeries had benefitted from the surgery).
In that, many specialists have concluded Botulinum Toxin treatment is the
only and the best treatment so far for this disease.
Another surgical approach was made by Dr. Genack & Dr. Woo in 1993.
They have performed Vocalis muscle cordotomy dissecting a small portion of vocal folds muscles
and then Dr. Watanabe has modified the surgery by adding the laser treatment and by transplanting the fat.
Dr. Woo’s approach was not of success but Dr. Watanabe’s approach was of a great success.
According to the dissecting method, laser could be in use,
however, one of its side effects is a hoarse voice. To get rid
of this problem, fat injection is being in use but the long-term
effect of this surgery is to be observed more.
In 1993, Dr. Berke has reported the ‘optional nerve
laryngectomy’ and in 1989 Dr. Friendman has tried the
surgery technique by using the technique of a nerve
stimulator transplantation.
To conclude, Botulinum Toxin injection is considered as the best
remedy for treating spasmodic dysphonia.